ANATOMY – TRICEPS MUSCLE
Click on Image to Enlarge
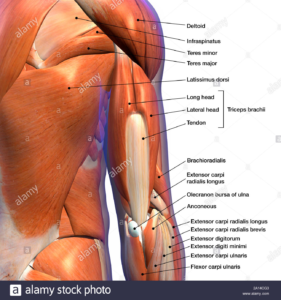
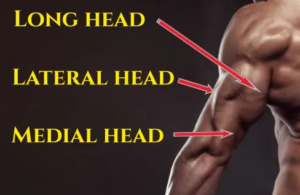
Long Head
- Origin: infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula
- Insertion: Posterior surface of the olecranon process of the ulna, capsule of the elbow joint and antebrachial fascia.
- Action: Because it attaches to the scapula, the long head not only extends the elbow but will also have a small action on the glenohumeral joint. With the arm adducted, the triceps muscle acts to hold the head of the humerus in the glenoid cavity. This action helps prevent any displacement of the humerus. The long head also assists with the extension and adduction of the arm at the shoulder joint. The lateral head is also active during extension of the forearm at the elbow joint when the forearm is supinated or pronated.
- Innervation: radial nerve
Lateral Head
- Origin: posterior aspect of the humerus, superior to the radial groove
- Insertion: Posterior surface of the olecranon process of the ulna, capsule of the elbow joint and antebrachial fascia.
- Action: Strongest head of the three. It is active during extension of the forearm at the elbow joint when the forearm is supinated or pronated.
- Innervation: radial nerve
Medial Head
- Origin: posterior aspect of humerus, inferior to the radial groove
- Insertion: Posterior surface of the olecranon process of the ulna, capsule of the elbow joint and antebrachial fascia.
- Action: The medial head does not attach to the scapula and therefore has no action on the glenohumeral joint, whether with stabilization or movement. However, the medial head is active during extension of the forearm at the elbow joint when the forearm is supinated or pronated.
- Innervation: radial nerve
Note: All the three heads of triceps brachii are innervated by the four branches of the radial nerve (C7, C8). However, according to the cadaveric study it is found that the medial head of triceps brachii is innervated by the ulnar nerve.[4]. Some research reveals that the long head of triceps is actually innervated by the axillary nerve.[5]
YOUTUBE VIDEOS
- NOTED ANATOMIST – ELBOW JOINT – MUSCLES & NERVES .
- WEBSTER – MUSCLES OF THE UPPER ARM .
- ANATOMY ZONE – TRICEPS .