BB – BARBELL ROWS
Click on Image to Enlarge
MOMENT ARM & EMG STUDY
LATISSIMUS DORSI MIDDLE REGION, UPPER & LOWER ERECTOR SPINAE
JOINT COMPRESSION, AXIAL TWIST & FLEXION-EXT MUSCULAR STIFFNESS
– Inverted Body Row, Standing 1-Arm Cable Row, BB Row
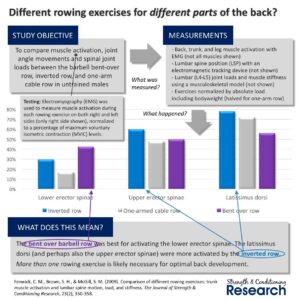
Comparison of Different Rowing Exercises: Trunk Muscle Activation and Lumbar Spine Motion, Load, and Stiffness – 2009 – Fenwick, McGill
Procedures
– matched the loading between exercises relative to inverted row
– All subjects were recreationally active; however, the tasks were novel to some of the participants.
Electrode Placement
– Latissimus Dorsi: over the muscle belly when the arm was positioned in the shoulder mid-range
Results
Latissimus Dorsi – Middle: inverted row 80% · standing 1-arm cable row 70% · bent over bb row 55%
+ Upper erector Spinae: inverted row 60% · bent over bb row 50% · standing 1-arm cable row 50%
+ Lower erector Spinae: bent over bb row 40% · inverted row 30% · standing 1-arm cable row 20%
Results – Figure 4 below
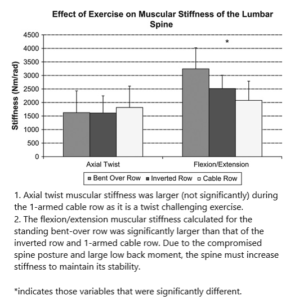
Joint Compression: bent over bb row · standing 1-arm cable row · inverted row
– the compromised spine angle and large moment caused by the load in the hand contributed to the high joint compression
Result Figure 5 below
Axial Twist Muscular Stiffness: standing 1-arm cable row · bent over bb row · inverted row
Flexion/Extension Muscular Stiffness: bent-over bb row · inverted row · standing 1-armed cable row
– Due to compromised spine posture and large low back moment, the spine must increase stiffness to maintain its stability
EMG STUDIES
LATISSIMUS DORSI, UPPER-MIDDLE-LOWER TRAPS & BICEPS
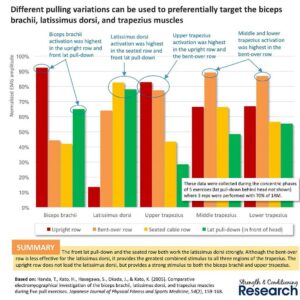
– Seated Cable Row, BB Row, Lat Pulldown, Upright Row
EMG of the biceps brachii, latissimus dorsi, and trapezius muscles during 5 pull exercises – 2005 – Handa
Procedure
– compare 5 different pull movements; 8 weight-trained men
Results using a Universal Machine – 3 reps @70%RM
Note: I don’t know where the electrodes were placed for the latissimus dorsi
Latissimus Dorsi: seated cable row 82% · lat pulldown 78% · bb bent over row 64% · upright row 14%
Trapezius – Upper: upright row 82% · bb bent over row 78% · seated cable row 42% · lat pulldown 29%
Trapezius – Middle: bb bent over row 90% · seated cable row 66% · upright row 66% · lat pulldown 48%
Trapezius – Lower: bb bent over row 87% · upright row 67% · seated cable row 56% · lat pulldown 55%
+ Biceps Brachii: upright row 92% · lat pulldown 64% · bb bent over row 44% · seated cable row 41%
UPPER LATS, INFRASPINATUS, MIDDLE-LOWER TRAPS & ERECTOR SPINAE
– Seated Cable Row, Inverted Body Row, Prone LYT, BB Row
– Lat Pulldown, Chinup, Pullup
 What is the best back exercise? – 2018 – Edelburg – PDF Link to Edelburg Thesis .
What is the best back exercise? – 2018 – Edelburg – PDF Link to Edelburg Thesis .
Procedure
– 19 males; resistance-trained; 5 reps @70% 1RM or bodywt; rest 2min; exercises performed in random order
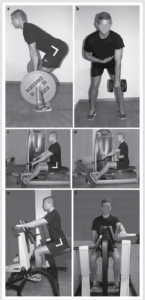
Lat Pulldown: overhand grip; medium width
Pullup: pronated overhand grip; medium width; Chinup: supinated underhand grip; shoulder width
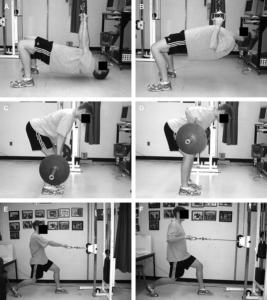
Bent-over BB Row: overhand grip; wrists, elbows shoulders straight line; pulled toward the sternum keeping a flat back
Inverted row: medium-width grip; body straight, heels on floor, arms fully extended; pulled chest toward bar; shoulder blades retracted
Seated Row: Seated pulley machine; V-bar handle; feet on platform, knees bent, straight back; chest up; elbows back to front of stomach
I-Y-T Raises: prone on bench; palms facing for the letter “I”, palms facing for the letter “Y”, palms facing the floor for the letter “T”
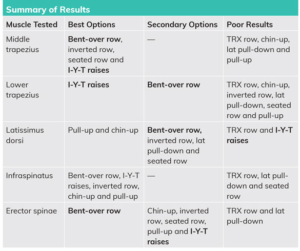
Results MVC
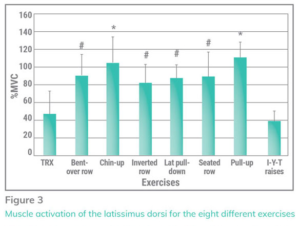
Latissimus dorsi – Upper Fibers – Extension, adduction, horizontal abduction, and internal rotation of the shoulder
· Over 100% – pullup > chinup
· 85% → 82% – bent-over bb row > seated row > lat pulldown > inverted row
· 45% → 40% –TRX > IYT
Infraspinatus – External rotation of the shoulder (this is one of the rotator cuff muscles)
· 58% → 50% –IYT> bent over bb row > pullup > chinup > inverted row
· 40% → 35% – seated row > TRX> lat pulldown
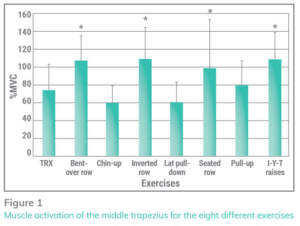
Middle trapezius – Upward rotation and adduction of the scapulae
· Over 100% – IYT > bent over bb row > inverted row > seated row
· 80% → 75% – pullup> TRX
· 60% – chinup > lat pulldown
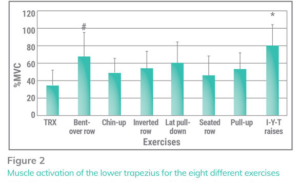
Lower trapezius – Depression of the scapulae
· 80% – IYT
· 62% → 42% – bent over bb row>lat pulldown > pullup >inverted row > chinup> seated row
· 35% – TRX
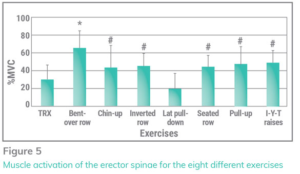
+ Erector spinae – Extension and lateral flexion of the spine
· 62% – bent over bb row
· 48% → 40% – IYT > pullup > chinup > inverted row > seated row
· 28% → 20% – TRX> lat pulldown
The effect of bilateral and unilateral row exercises on core muscle activation · 2015 – Saeterbakken; Vidar Andersen
Procedure
– 15 resistance-trained men
Results
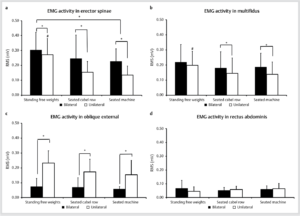
Erector spinae: bb row 30% · db row 28% · seated cable bilateral 25% · machine bilateral 25% · seated cable unilateral 15% · machine unilateral 12%
Multifidus: bb row 22% · db row 22% · machine bilateral 20% · seated cable bilateral 18% · seated cable unilateral 15% · machine unilateral 15%
External oblique: db row 25% · seated cable unilateral 15% · machine unilateral 15%
Rectus abdominis: no significant differences