LOWER LEG – POSTERIOR – TRAINING RESEARCH
Click on Image to Enlarge
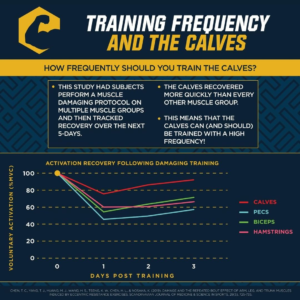
TRAINING – ACHILLES TENDON
MUSCLE MASS PROGRAM
LATERAL & MEDIAL GASTROCNEMIUS, SOLEUS
– Angle of the Toes
Different Foot Positioning During Calf Training to Induce Portion-Specific Gastrocnemius Muscle Hypertrophy – 2020 – Nunes
Procedure
– 22 men performed a whole-body resistance training program 3x/wk for nine weeks, with differences in the exercise specific for calves
– Calf-raise exercise was performed unilaterally, in a pin-loaded seated horizontal leg-press machine, in 3 sets x 20-25 reps for training wks 1-3, and 4 sets for wks 4-9
Results – % change after training
Lateral Gastrocnemius: Toes Inward 8.9% . Toes Forward 6.3% . Toes Outward 5.3%
Medial Gastrocnemius: Toes Outward 8.0% . Toes Forward 6.0% . Toes Inward 5.0%
EMG STUDIES
LATERAL & MEDIAL GASTROCNEMIUS, SOLEUS
– 8 Exercises
Electromyographic Analysis of the Triceps Surae Muscle Complex During Achilles Tendon Rehabilitation Program Exercises – 2011 – Mullaney
Procedure
– 20 healthy lower extremities (10 participants, 27 ± 5 yrs old)
– Muscle activity was recorded during 8 therapeutic exercises commonly used following an Achilles repair
– Maximal voluntary isometric contractions (MVICs) were also performed on an isokinetic device
– Each exercise was performed for 8 to 10 repetitions to the pace of a metronome to keep pace consistent (1.5 secs per cycle)
Electrodes
– medial head of the gastrocnemius
– lateral head of the gastrocnemius
– soleus
Exercises – MVIC
1. Hopping: single-leg jumps: 130%
2. Heel Raises: single-limb: 110%
3. Lateral Step-ups: 60%
4. Walking: 48%
5. Supine Plantarflexion with red TheraBand: 42%
6. Prone Ankle Pumps: 38%
7. Single-leg balance on wobble board: 22%
8. Seated Toe Raises: 9%
LATERAL & MEDIAL GASTROCNEMIUS, SOLEUS
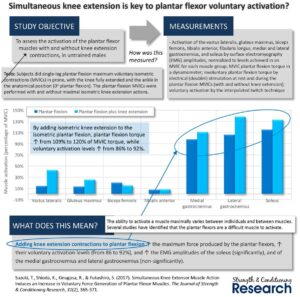
– Plantar Flexion combined with Knee Extension
Simultaneous Knee Extensor Muscle Action Induces an Increase in Voluntary Force Generation of Plantar Flexor Muscles – 2016 – Suzuki
Procedure
– We hypothesized that coactivation of the plantar flexor muscles and knee extensor muscles would result in a higher plantar flexion torque
– 8 male volunteers performed maximum voluntary isometric action of the plantar flexor muscles with and without isometric action of the knee extensor muscles
Results
Medial Gastrocnemius: 98% to 111%
Lateral Gastrocnemius: 106% to 138%
Soleus: 115% to 133%
– The resultant plantar flexion torque also significantly increased by 11.5% of the predetermined maximum